At Pressure And Temperature Ideal Gas Particles Tend To Stop Behaving Ideally
(KE) ave = (2/3)RT As the temperature increases, the average kinetic energy increases as does the velocity of the gas particles.
At pressure and temperature ideal gas particles tend to stop behaving ideally. The relationship is linear, if the temperature of a volume of gas doubles, the volume doubles. In general, the deviations from ideal behavior increase as temperature decreases, becoming significant near the temperature at which the gas is converted into a liquid. The degree to which a gas sample deviates from the ideal gas law will grow and shrink continuously depending on the state parameters, but the deviations will never go away entirely;.
The effect is that increase in temperature increases the kinetic energy of gas molecules, making them move more faster and vibrate more. Real gases do not always follow the assumptions of the kinetic molecular theory. Vapour pressure of a pure compound is the pressure characteristic at any given temperature of a vapour in equilibrium with its liquid or solid form.
The deviations from ideal gas behaviour can be illustrated as follows:. At low pressure and high temperature, real gases behave approximately as ideal gases. Gases that deviate from ideality are known as Real Gases, which originate from two factors:.
As pressure increases or the temperature drops, intermolecular forces between gas molecules become more important. Ideal gas law relation between the pressure, volume, amount, and temperature of a gas under conditions derived by combination of the simple gas laws standard conditions of temperature and pressure (STP) 273.15 K (0 °C) and 1 atm (101.325 kPa) standard molar volume volume of 1 mole of gas at STP, approximately 22.4 L for gases behaving ideally. I want to understand this - When pressure is low attractive forces in the gas moelcules will be stronger(as compared to high pressure) but the fast movement due to high temperature compensates it.
Pressure, Volume, and Temperature Relationships in Real Gases. The volume of the gas particles is considered negligible;. The spatial distribution of temperature, density, pressure and chemical potential is studied in detail with and without the presence of gravitational forces.
(1) First, the theory assumes that as pressure increases, the volume of a gas becomes very small and approaches zero. Vapour pressure is a measure of the ability of a compound to bond with itself;. At constant pressure, when there is an increase in temperature the motion of the gas particles will increase.
The ideal gas equation predicts that the pressure would have to increase to 448 atm to condense 1.00 mole of CO 2 at 0 o C to a volume of 0.0500 L. P + a(n/V) 2 (V/n – b) = RT (8). One mole of an ideal gas has a capacity of 22. (13) litres at standard temperature and pressure (a temperature of 273.15 K and an absolute pressure of exactly 10 5 Pa) as defined by IUPAC since 19.
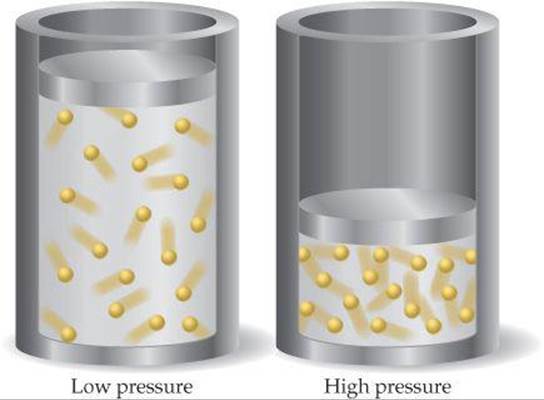
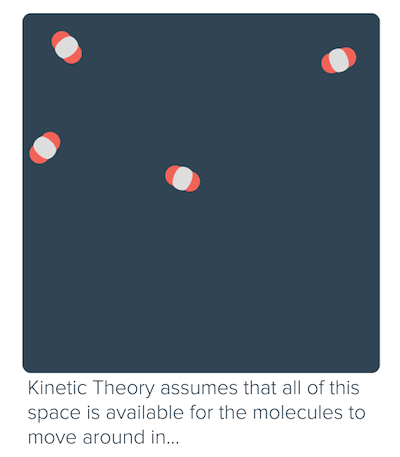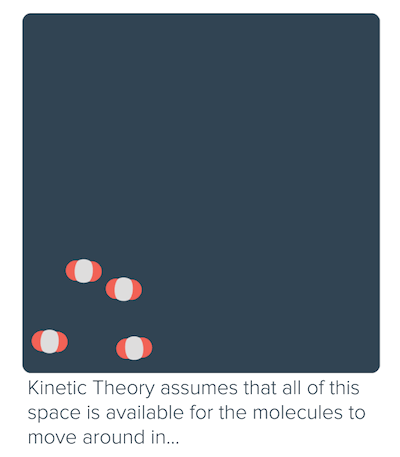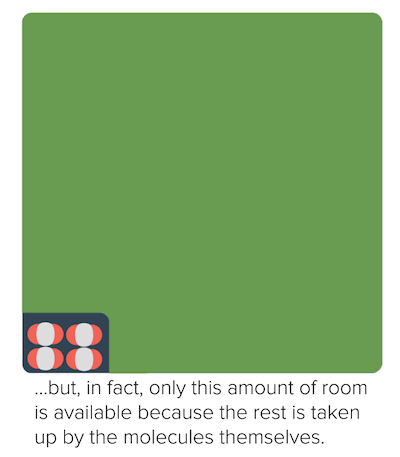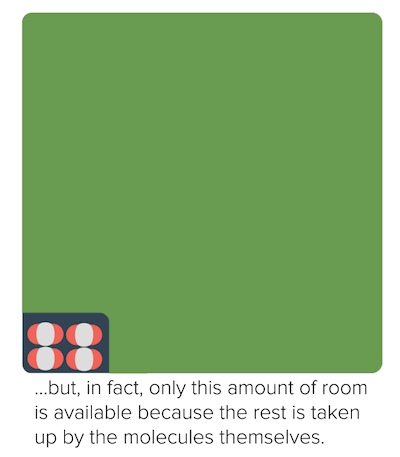
The idea that matter is made up of small particles that are in constant motion is ___. As the pressure increases, the gas compresses, the particles come closer reducing the volume of gas. While the particles of an ideal gas are assumed to occupy no volume and experience no interparticle attractions, the particles of a real gas do have finite volumes and do attract one another.
However they show deviations from ideality at low temperatures and high pressures. The van der Waals equation predicts that the pressure will have to reach 16 atm to achieve the same results. Let's now compress the gas even further, raising the pressure until the volume of the gas is only 0.0500 liters.
Well i know real gases behave as ideal gas (almost) when pressure is low and temperature is high. And, of course, you could redo this calculation to find the volume of 1 mole of an ideal gas at room temperature and pressure - or any other temperature and pressure. This is the currently selected item.
This is about as tricky as it gets using the ideal gas. There's nowhere that it. But in reality this is not the case:.
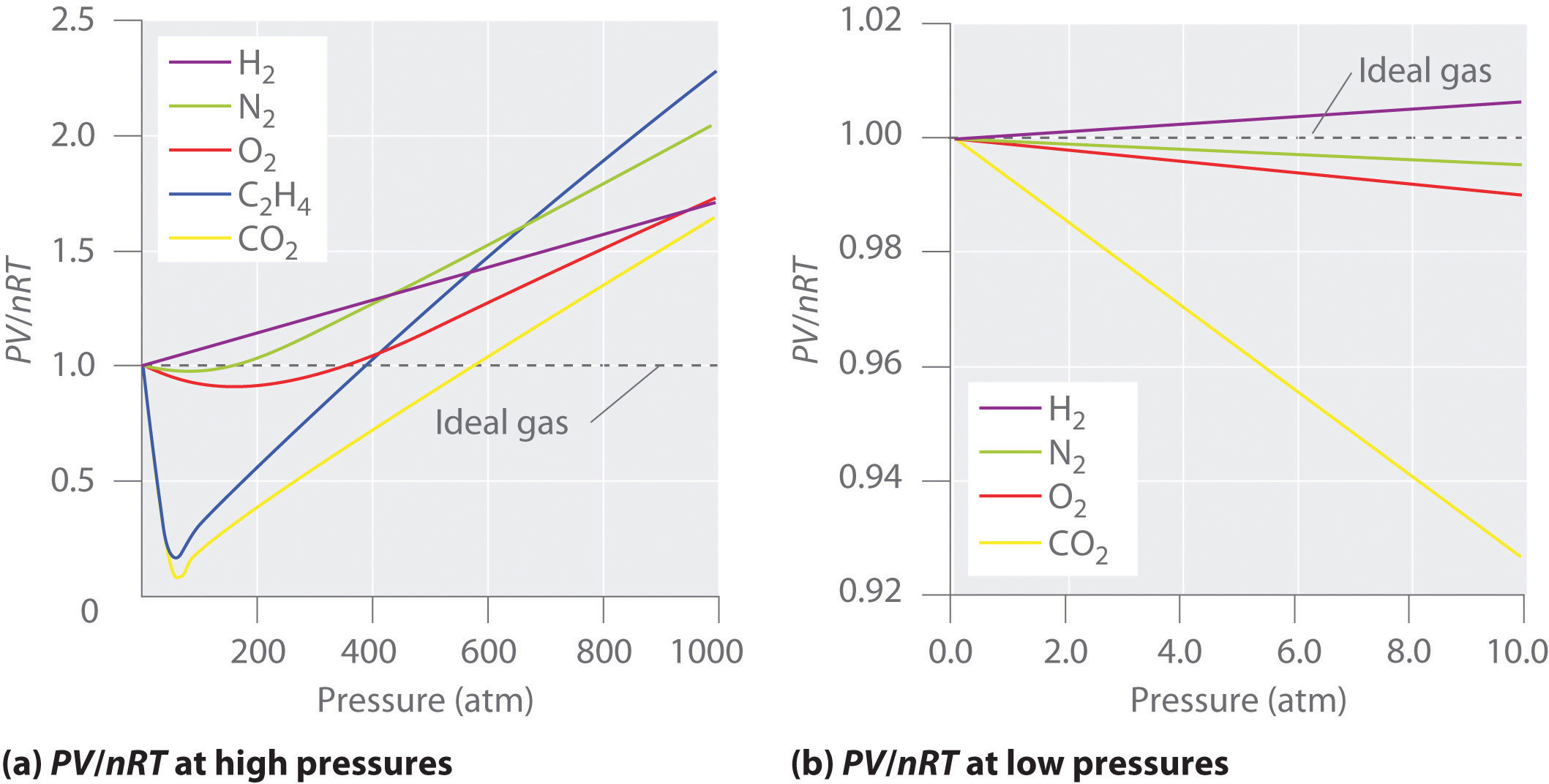
In general, the internal energy is a function of two variables, since the dependence on third is given by the state equation. Gases and Atmospheric Chemistry;. (i) Interpret the behaviour of real gas with respect to an ideal gas at low pressure.
Joule-Thomson effect is zero in an ideal gas and enthalpy remains constant. That is nuts of course. Gases and Atmospheric Chemistry The ABC's of Gases 1662:.
When an ideal gas expands in vacuum, it does no work i.e. The molar volume of an ideal gas is therefore 22.4 dm 3 at stp. C) Pressure will compress a gas, reducing its volume and giving it a greater density and concentration of particles.
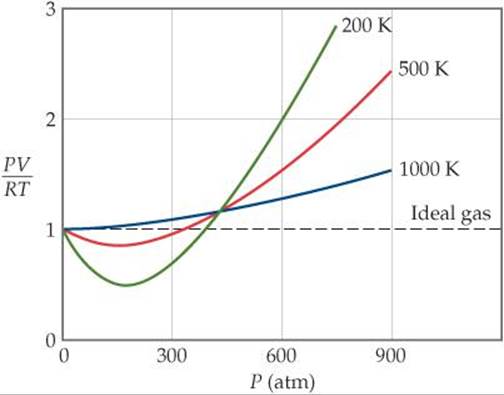
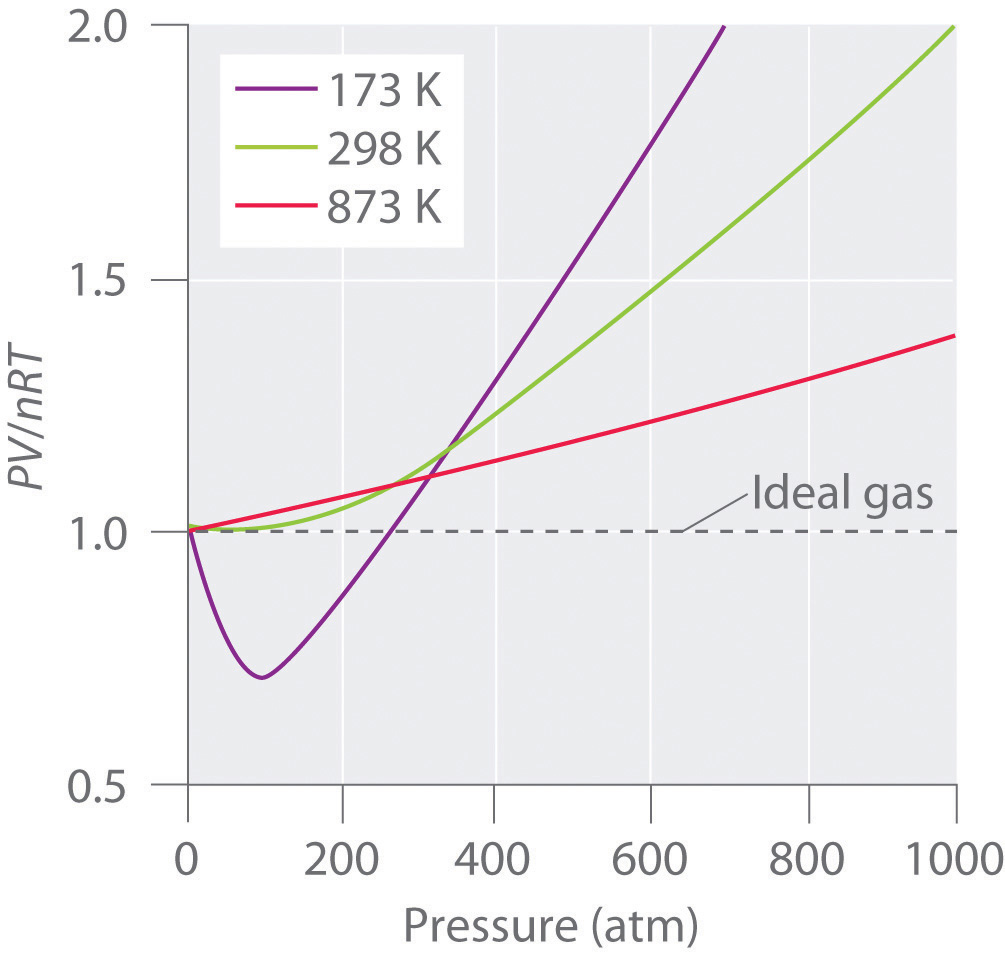
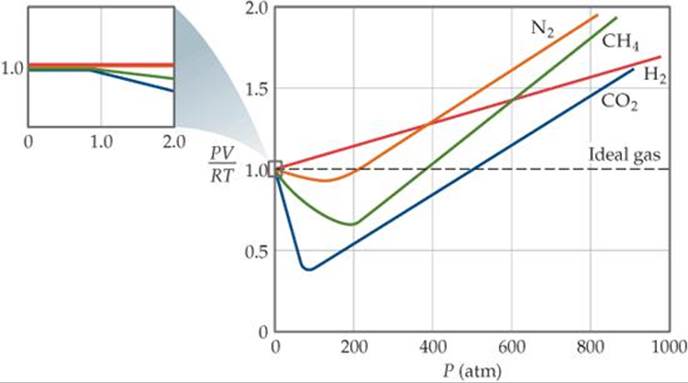
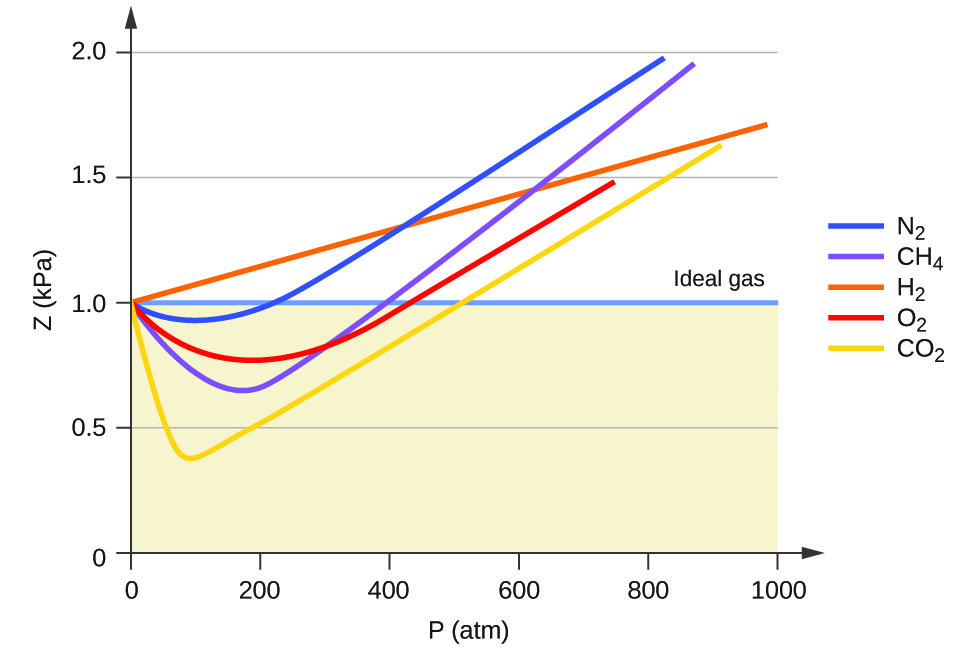
FIGURE 10.21 PV/RT versus pressure for 1 mol of nitrogen gas at three different temperatures. Inversion temperature for hydrogen = –80°C and for He = –240°C. In cold gases, the particles move relatively slowly.
If gases are not ideally behaving in room temperature and pressure almost close to 1 atm, they are called real gases. In an ideal gas, there is no molecule-molecule interaction, and only elastic collisions are allowed. For an ideal gas, a plot of PV/nRT versus P gives a horizontal line with an intercept of 1 on the PV/nRT axis.
Real gases are not point particles, and no real gases behave ideally. Avogadro's Hypothesis (V N) As the number of gas particles increases, the frequency of collisions with the walls of the container must increase. Gas is one of the four fundamental states of matter (the others being solid, liquid, and plasma).A pure gas may be made up of individual atoms (e.g.
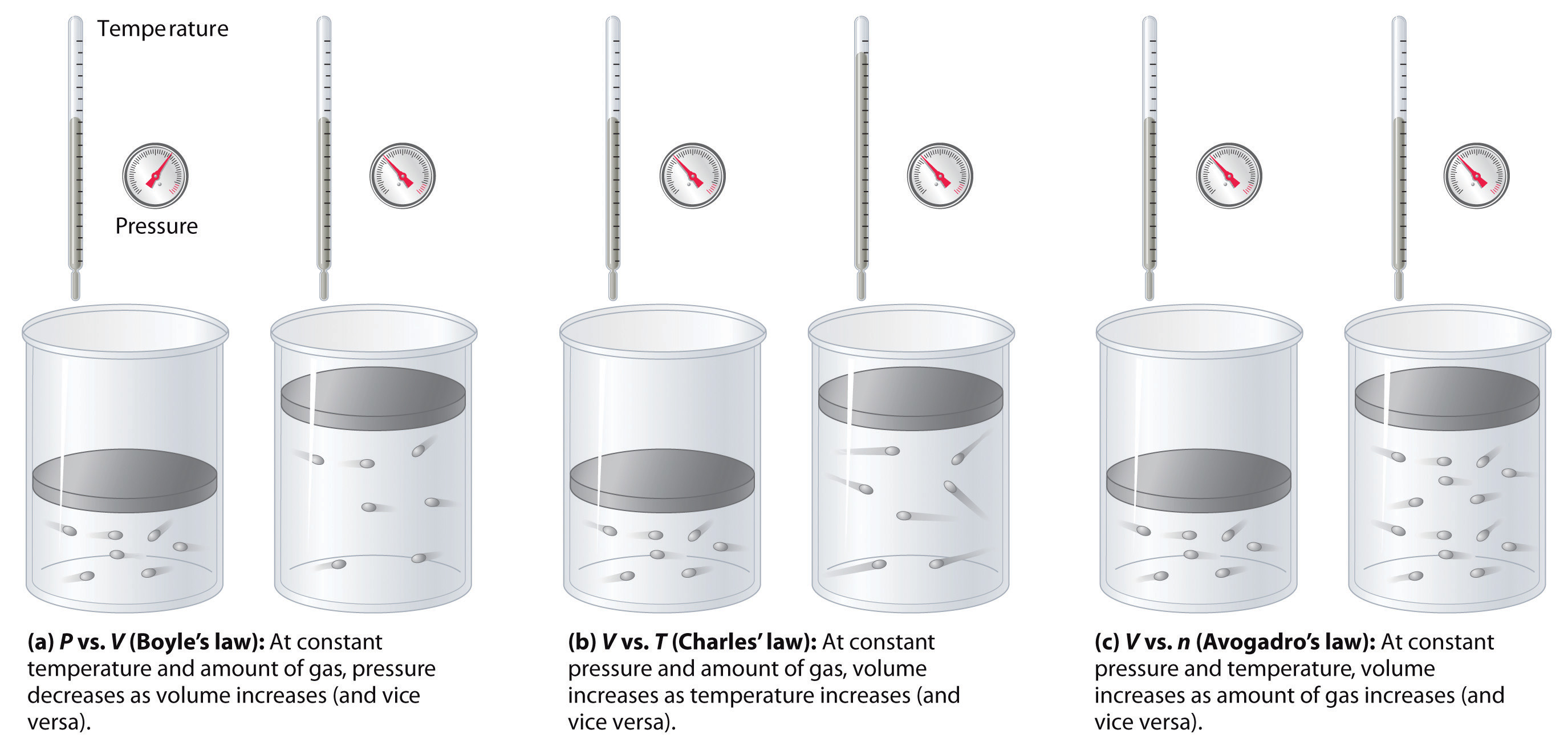
A gas, behaving ideally, fills a fixed volume container at a pressure P1 and at a temperature T1. Using Avogadro's, Charles', or Boyle's law, develop an expression that would solve for the new pressure P2. Assuming all of the following samples behave as ideal gases and that they are all at the same temperature, which will have the greatest pressure?.
In the microscopic view of an ideal gas, the temperature is zero when the average kinetic energy of the ideal gas is zero. Answer the following questions based on this graph. The ABC’s of Gases.
As temperature increases, the gas more closely approaches ideal behavior. (ii) Interpret the behaviour of real gas with respect to an ideal gas at high pressure. At low temperatures, the gas particles have lower kinetic energy and do not move as fast.
Have no attractive forces between them;. Epaminondas Voutsas, in Thermodynamics, Solubility and Environmental Issues, 07. Ocabanga44 and 281 more users found this answer helpful.
Pressure versus volume graph for a real gas and an ideal gas is shown in Fig. Gases, Liquids, and Solids. The pressure–volume product, rather than energy per temperature increment per particle.The constant is also a combination of the constants from Boyle's law, Charles's law, Avogadro's law, and Gay-Lussac's law.
The proportionality constant is (2/3)R and R is the gas constant with a value of 0.006 L atm K-1 mol-1 or 8.3145 J K-1 mol-1. Absolute zero in the Kelvin scale is the point at which the pressure drops to zero. Pressure The pressure of a gas is defined as the force exerted by that gas on an area.
If greater pressure is applied, the water will go from the more concentrated solution to a less concentrated (more pure) solution. The amount of gas. If temperature is held constant, the equation is reduced to Boyle's law.
$\begingroup$ No physical gas ever behaves exactly like an ideal gas;. A noble gas like neon), elemental molecules made from one type of atom (e.g. Real gases do not obey ideal gas equation under all conditions.
If you fit data from just a small pressure and temperature range to get the best fit "a" and "b" constants for the van der Walls equation then you could easily get a negative "a" term. 41 10.) (cont.) 10.) a) Gases behave non-ideally at HIGH Pressure and LOW Temp (Real gases behave ideally at low P and high T) b) Real gases behave non-ideally because they have:. As a result, real gases are often observed to deviate from ideal behavior.
Flexible containers, such as a balloon, will. Attractions prevent the ions from behaving as totally independent particles (Figure 11. This, in turn, leads to an increase in the pressure of the gas.
Ideal gas is a toy model to understand the behavior of real gases and furnishes a lot of nice results to begin with. Ideal Gases Versus Real Gases. At higher temperatures, the average speed increases.
Under these conditions, the ideal gas law is replaced by the van der Waals equation. Hence internal energy of a given quantity of an ideal gas at constant temperature is independent of its volume. The Ideal Gas Law applies to ideal gases.An ideal gas contains molecules of a negligible size that have an average molar kinetic energy that depends only on temperature.
The ideal gas law is the equation of state of a hypothetical ideal gas (an illustration is offered in ). Avogadro's number Standard Temperature and Pressure STP is used widely as a standard reference point for expression of the properties and processes of ideal gases. An increase in temperature increases the distance between gas particles.
Compound molecules that bond well with each other will have a. Vapor pressure and the ideal gas law. A gas law that states for a fixed amount of gas at constant volume, the pressure of the gas is proportional to its Kelvin temperature ideal gas law a gas law that relates the pressure, volume, temperature, and number of moles of a gas in a single equation;.
It is a good approximation to the behavior of many gases under many conditions, although it has several limitations. Intermolecular forces and molecular size are not considered by the Ideal Gas Law. Have volume) and cannot be compressed.
Non-ideal behavior of gases. How real gases differ from ideal gases, and when intermolecular attractions and gas molecule volume matter. The gas constant is denoted by the symbol R or R.It is equivalent to the Boltzmann constant, but expressed in units of energy per temperature increment per mole, i.e.
The ideal gas law (like almost every law of physics) is an approximation that holds under certain idealized assumptions. Assume that the mass of the particle is proportional to its size. $\begingroup$ You have to understand that the ideal gas model and the van der Walls model are supposed to work from a temperature of zero to infinity and pressure from zero to infinity.
Therefore, if you decrease the pressure of a fixed amount of gas, its volume will increase. The volume of the gas therefore becomes larger as the temperature of the gas increases. In ideal behaviour, gas particles don't occupy space and do not have any interaction, as assumed in the kinetic theory of gases.
Finding the relative formula mass of a gas from its density. Are in random, constant, straight-line motion, are separated by great distances relative to their size;. Ideal Gas Law question.picture included?.
The Van der Waals equation is the corrected equation of the ideal gas equation. PV = nRT Pressure, Volume, Temperature, Moles We know that temperature is proportional to the average kinetic energy of a sample of gas. Osmotic pressure is the amount of pressure that must be applied to the more concentrated solution to cause osmosis to stop.
We get errors by applying the ideal gas law. Have collisions that may result in the transfer of energy between particles, but the total energy of the. Oxygen), or compound molecules made from a variety of atoms (e.g.
Robert Boyle's Law allows chemists to predict the volume of any gas (behaving ideally) at any given pressure because relationship is always the same Inverse proportions (changes at the same rate for every gas 1780:. The particles that make up a solid move_____ than the particles that make up a gas:. Kinetic molecular theory (KMT) for an ideal gas states that all gas particles (3.4b):.
P V = constant. Cracking the SAT Chemistry Subject Test. An ideal gas is a theoretical gas that follows a set of principles.
Understanding what, on the molecular level, affects a substance's phase and how a substance goes about changing from one phase to the next is necessary for the SAT Chemistry Test. The force arises from the collisions of gas particles. For most gases at temperatures near (or above) room temperature (298 K = 25 o C) and near (or below) room pressure (1 atm = 760 torr), the ideal gas law adequately describes the behavior of the gas:.
Real gas particles occupy some of the volume of the container so the volume of free space for the molecules to move in is less than the container (causes P measured > P ideal) - Positive deviations. The Ideal Gas Law applies best to monoatomic gases at low pressure and high temperature. Generally, a gas behaves more like an ideal gas at higher temperature and lower pressure, as the potential energy due to intermolecular forces becomes less significant compared with the particles' kinetic energy, and the size of the molecules becomes less significant compared to the empty space between them.
While Charles' Law describes the behavior of ideal gases, not real ones, the law does have real-world applications. A numerical study of the ideal monoatomic gas in a rectangular ☐ is presented. Allows chemists to predict the volume of any gas (behaving ideally) at any given pressure because relationship is always the same.
The kinetic theory of matter:. Carbon dioxide).A gas mixture, such as air, contains a variety of pure gases. At constant temperature, pressure and volume are inversely related.
As the temperature of a gas increases, the volume of the gas will _____ if the pressure remains that same:. For this relationship to hold, both the mass of the gas and its pressure are held constant, and the temperature must be reported in Kelvin. It sounds very complicated, but this theory is just a.
The combined gas law states that the pressure of a gas is inversely related to the volume and directly related to the temperature. Phase refers to whether a substance is a solid, liquid, or gas. Jacques Charles' Law noticed a different relationship between gas and their….
Where R = 0.006 L atm mol -1 K -1 is a constant of nature called the ideal gas constant. The gas particles are affected by the intermolecular forces acting on them, which leads to inelastic collisions between them. Some conclusions are drawn regarding the importance of the particle-wall interaction.
For the most part, you can apply the ideal gas law to gases at high temperatures (room temperature and higher) and low pressures. These principles are part of a model called the kinetic molecular theory. Real gases, however, show significant deviations from the behavior expected for an ideal gas, particularly at high pressures (part (a) in Figure 10.21 "Real Gases Do Not Obey the Ideal Gas Law, Especially at High Pressures").
The temperature of a gas (in K) is a measure of the average speed of its atoms or molecules. While it does approach a small number, it will not be zero because molecules do occupy space (i.e. Pressure vanished because the molecules no longer mover around and bounce against the walls.
This leads to fewer collisions with the container and a lower pressure than what is expected from an ideal gas. One mole of an ideal gas will occupy a volume of 22.4 liters at STP (Standard Temperature and Pressure, 0°C and one atmosphere pressure). The ideal gas model tends to fail at lower temperatures or higher pressures, when intermolecular forces and molecular size becomes important.
They nearly obey ideal gas equation at higher temperatures and very low pressures. The temperature of the container is changed to T2.

Ncert Chemistry States Of Matter Dronstudy Com

Vapour Pressure An Overview Sciencedirect Topics
Cnx Org Exports 34fdcebf B956 4d65 84 Ecb12bca42 2 48 Pdf Derived Copy Of University Physics Volume 3 2 48 Pdf
At Pressure And Temperature Ideal Gas Particles Tend To Stop Behaving Ideally のギャラリー
When Does Real Gas Behave As Ideal Gas Quora

The Behavior Of Gases Chemistry For Non Majors
Www Cusd80 Com Cms Lib Az Centricity Domain 2137 Zumdahl chapter 5 gases Pdf

Real And Ideal Gases Ck 12 Foundation

Write Difference Between Ideal Gas Real Gas

Chemistry Behind Airbags

Deviation Of Gas From Ideal Behavior Boundless Chemistry
Q Tbn And9gcs7iqorfl98v4hppuodhaitflarlhgcw3vzs O9dvosjini0xc Usqp Cau
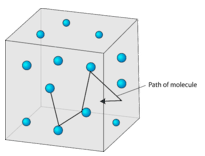
6 1 Kinetic Molecular Theory A Model For Gases Chemistry Libretexts
Http Vallance Chem Ox Ac Uk Pdfs Propertiesofgaseslecturenotes Pdf

Chapter 10 Section 9

Gas Laws 28 Chemistry Task Cards Gas Properties Manometers Graphs Problems
Dz I6tpqnpprlm
Http Vallance Chem Ox Ac Uk Pdfs Propertiesofgaseslecturenotes Pdf

Deviations From The Ideal Gas Law

Deviations From The Ideal Gas Law

The Behavior Of Gases Chemistry For Non Majors
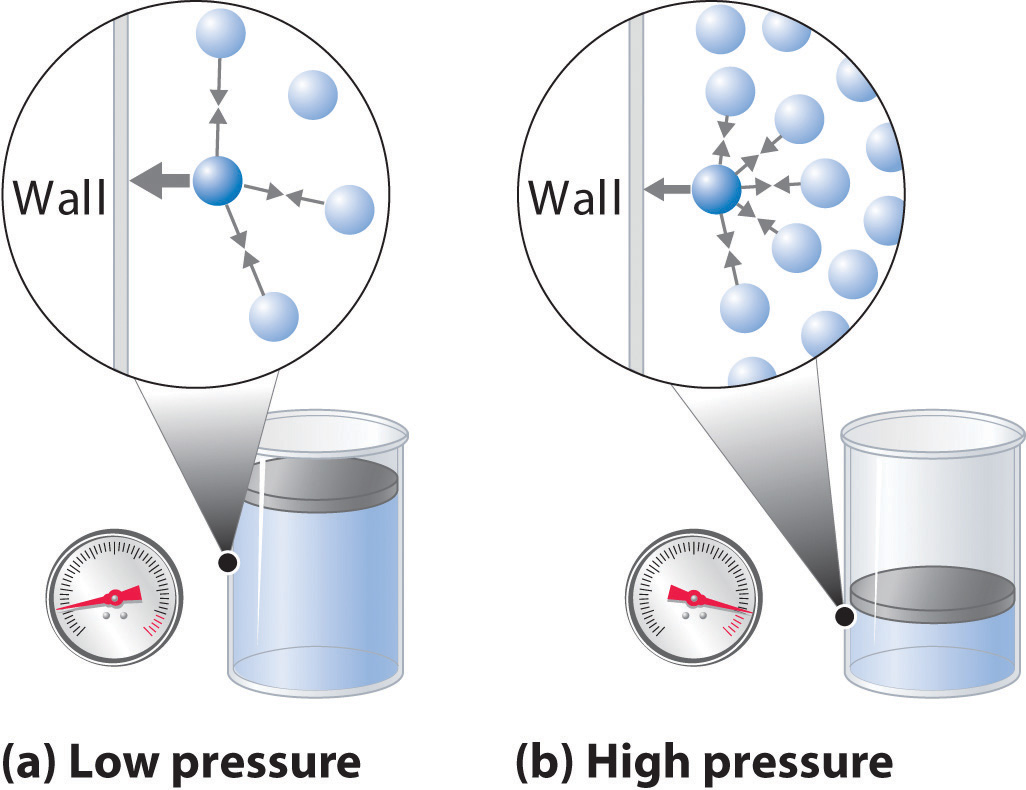
The Behavior Of Real Gases

Under What Conditions Do You Expect A Real Gas Such As Hydrogen Gas To Behave Like An Ideal Gas Quora

Properties Of Gases Claire Vallance
Courses Modernstates Org Assets Courseware 458fcfe2a9ea3cb07f043f7 Asset V1 Modernstatesx Chem1 16 T4 Type Asset Block S2 Pdf

Deviation Of Gas From Ideal Behavior Boundless Chemistry
Real Gases Deviations From Ideal Behavior Gases Chemistry The Central Science

Ncert Chemistry States Of Matter Dronstudy Com

Unit 1 Formerly Module 2 Ppt Download

Chemistry Behind Airbags

Unit 1 Formerly Module 2 Ppt Download

The Behavior Of Gases Chemistry For Non Majors

Chapter 10 Section 9

States Of Matter Miami Killian High School Powerpoint Presentation Free Online Download Ppt Aggszt

The Behavior Of Gases Chemistry For Non Majors
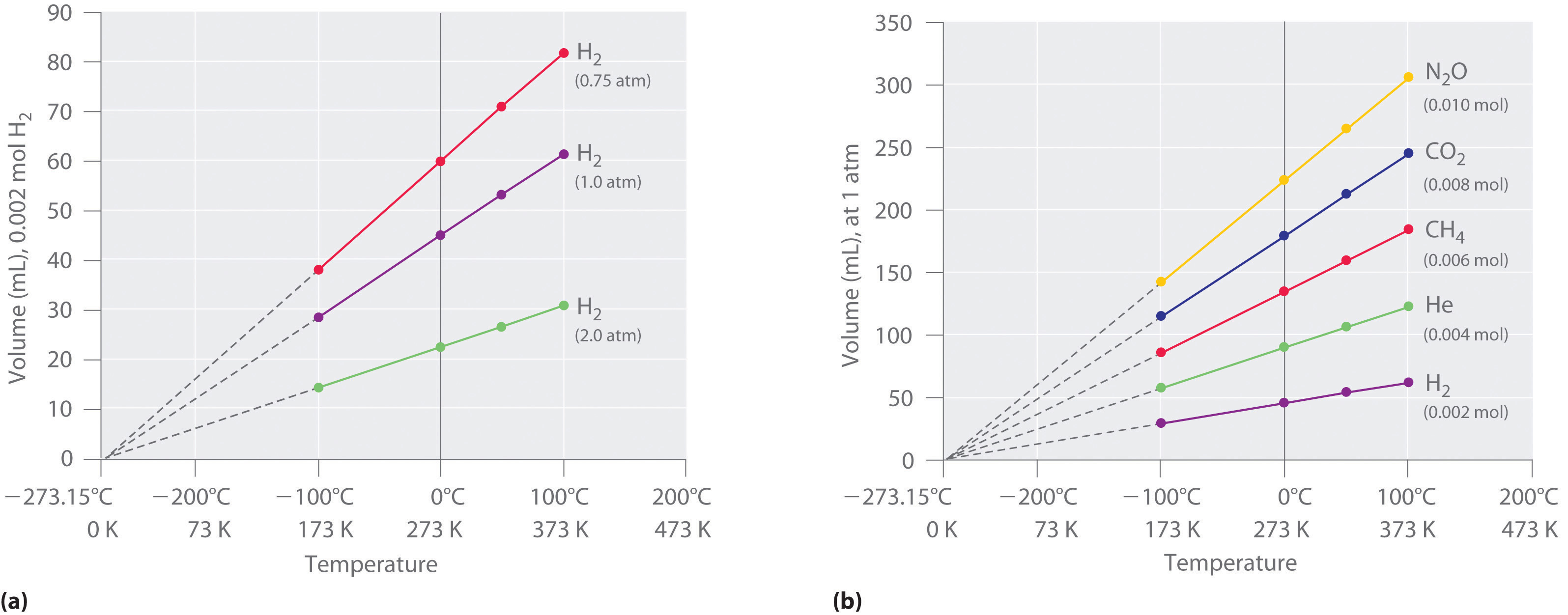
5 3 The Simple Gas Laws Boyle S Law Charles S Law And Avogadro S Law Chemistry Libretexts
Is Nitrogen An Ideal Gas Why Or Why Not Quora
Charles Law
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/186450350-56a132cb5f9b58b7d0bcf751.jpg)
What Is The Most Ideal Gas

Deviation Of Gas From Ideal Behavior Boundless Chemistry
Http Vallance Chem Ox Ac Uk Pdfs Propertiesofgaseslecturenotes Pdf
Q Tbn And9gcsboeoawribf1pnyobmtfljop4qbnofomxbp58czghebdkgjwur Usqp Cau

Absolute Zero Definition Facts Britannica

Chapter 10 Section 9

The Behavior Of Gases Chemistry For Non Majors
Cnx Org Exports 34fdcebf B956 4d65 84 Ecb12bca42 2 48 Pdf Derived Copy Of University Physics Volume 3 2 48 Pdf
Http Www Lcps Org Cms Lib4 Va Centricity Domain Packet gas laws Pdf
Q Tbn And9gcrp Cltrfuh4ynfy8bafkorne9rhjbpznf8phljtuidmaq Loiz Usqp Cau
Http Vallance Chem Ox Ac Uk Pdfs Propertiesofgaseslecturenotes Pdf
Http Vallance Chem Ox Ac Uk Pdfs Propertiesofgaseslecturenotes Pdf
Http Vallance Chem Ox Ac Uk Pdfs Propertiesofgaseslecturenotes Pdf

Charles Law
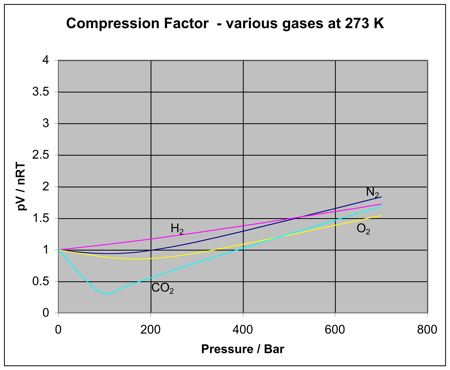
Non Ideal Behavior Of Gases Article Khan Academy
Tusd Learning Powerschool Com Eotis Thslibrary1 Cms File Show Pdf T
Ideal Gas Wikipedia

Non Ideal Behavior Of Gases Article Khan Academy

Ideal Gas Wikipedia

Under What Conditions Do You Expect A Real Gas Such As Hydrogen Gas To Behave Like An Ideal Gas Quora

The States Of Gases Chapter Ppt Download
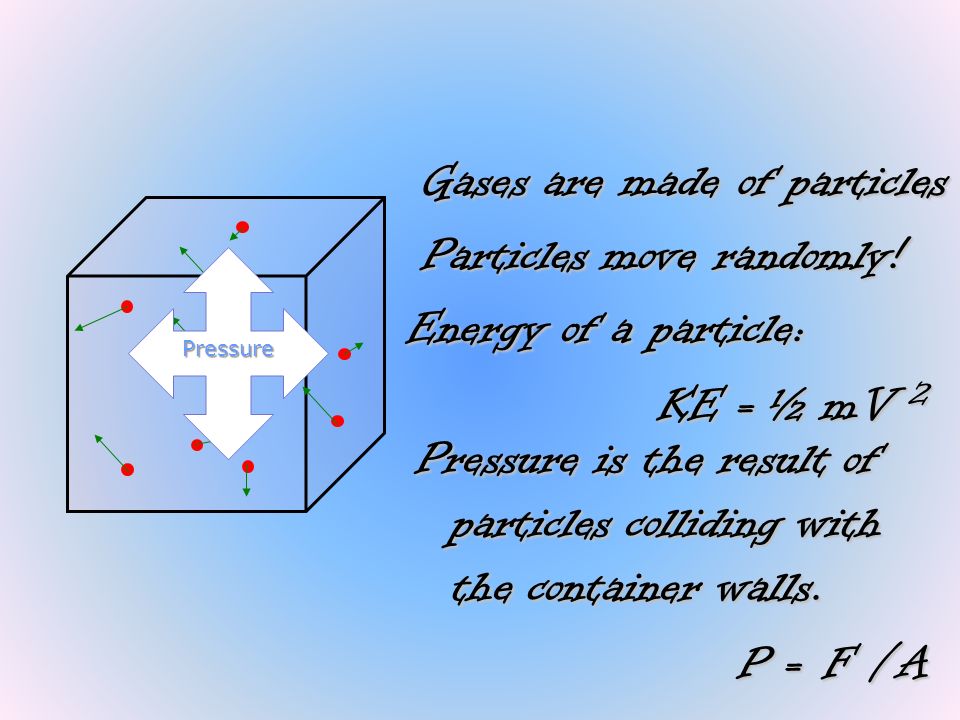
Gases And Their Applications Ppt Download
Real Gases Deviations From Ideal Behavior Gases Chemistry The Central Science
Www Basd K12 Wi Us Faculty Jdennert Chemtext Chapter 13 chemistry text Pdf

Gases And Their Applications Ppt Download
Q Tbn And9gcryhpaqx9urq Z7sebz1k7rgxbofvudjpsfxx 7gyg Usqp Cau
The Behavior Of Real Gases

Chapter 10 Section 9

Why Does A Real Gas Behave Like An Ideal Gas Only At Low Pressure And High Temperature Quora
Www Cusd80 Com Cms Lib Az Centricity Domain 2137 Zumdahl chapter 5 gases Pdf

11 Chemistrty New Book Pages 151 0 Flip Pdf Download Fliphtml5

Chem152 Ch 5 Pt2 Kinetic Molecular Theory Diffusion Effusion Real Gases Flashcards Quizlet

Pdf Engineering And Chemical Thermodynamics Pdf Hiren Patel Academia Edu
12books Lardbucket Org Pdfs Principles Of General Chemistry V1 0 S14 Gases Pdf

Under What Conditions Do You Expect A Real Gas Such As Hydrogen Gas To Behave Like An Ideal Gas Quora
Tusd Learning Powerschool Com Eotis Thslibrary1 Cms File Show Pdf T

Q Tbn And9gctv Nawze7jxbw2zhmkk Ulqavjfrcimnhkkw Usqp Cau
The Behavior Of Real Gases
Www Cusd80 Com Cms Lib Az Centricity Domain 2137 Zumdahl chapter 5 gases Pdf

Gases And Their Applications Ppt Download
Latest News Fluidflow Fluidflow

Unit 1 Formerly Module 2 Ppt Download
Q Tbn And9gctkn2c Hkvqfbxx9grsghymmc Zmfpwooynw Usqp Cau
Real Gases Deviations From Ideal Behavior Gases Chemistry The Central Science

Unit 1 Formerly Module 2 Ppt Download
Courses Modernstates Org Assets Courseware 458fcfe2a9ea3cb07f043f7 Asset V1 Modernstatesx Chem1 16 T4 Type Asset Block S2 Pdf

Properties Of Gases Claire Vallance

Deviations From The Ideal Gas Law
Www Basd K12 Wi Us Faculty Jdennert Chemtext Chapter 13 chemistry text Pdf

The Behavior Of Gases Chemistry For Non Majors
9 6 Non Ideal Gas Behavior Chemistry

Real Gases Deviations From Ideal Behavior Gases Chemistry The Central Science

The Kinetic Molecular Theory Properties Of Gases Video Lesson Transcript Study Com
Http Www Lcps Org Cms Lib4 Va Centricity Domain Packet gas laws Pdf

Chapter 10 Section 9
Gases
Www Cusd80 Com Cms Lib Az Centricity Domain 2137 Zumdahl chapter 5 gases Pdf

24 Physical Chemistry Crystal Structure Gases
Batch Libretexts Org Print Letter Finished Chem Full Pdf
Http Www Lcps Org Cms Lib4 Va Centricity Domain Packet gas laws Pdf

Properties Of Gases Dr Claire Vallance First Year Hilary Term Suggested Reading Pdf Free Download
Http Vallance Chem Ox Ac Uk Pdfs Propertiesofgaseslecturenotes Pdf

Gases And Their Applications Ppt Download

Real And Ideal Gases Ck 12 Foundation

Properties Of Gases Dr Claire Vallance First Year Hilary Term Suggested Reading Pdf Free Download

When Do Real Gases Act Like Ideal Gases Youtube

Mcat General Chemistry Quick Review And Overview Medical Math Chemistry Notes Chemistry




