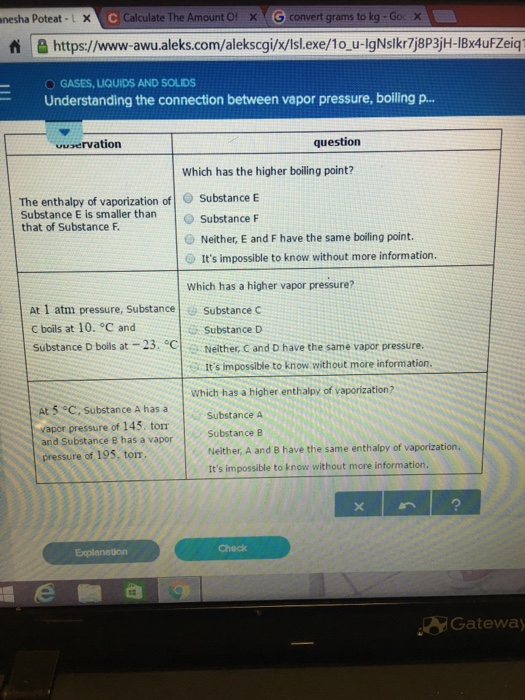
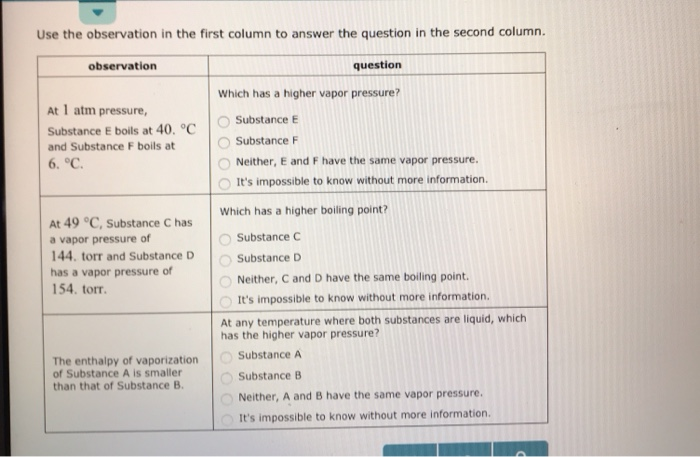
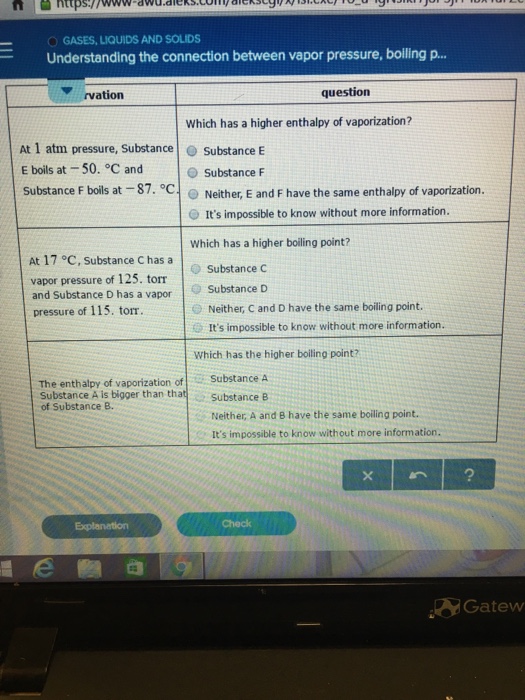
At Pressure Substance E Boils At And Substance F Boils At
Solution for If the pressure of a substance is increased during a boiling process, will the temperature also increase or will it remain constant?.

At pressure substance e boils at and substance f boils at. List the following substances in order of increasing normal boiling point:. It's impossible to know without more information. Jan 17, 15 · A liquid boils when its vapor pressure equals the exterior pressure, and since we're at 1 atm, that is what the vapor pressure for a substance at its boiling point will be.
Arrange these substances in order of INCREASING boiling point:. An increase in atmospheric pressure will lower the boiling point of a substance because the vapour pressure of the substance will be compensated by the external pressure at this temperature. There won't be any change because it is a saturation point.
This is known as. This pressure decreases with increasing elevation and hence the boiling point of a liquid also decreases. It's impossible to know without more information.
It's impossible to know without more information. Up a mountain water. A) Xe H 2 H 2 O LiCl H 2 S b) Xe H 2 H 2 S H 2 O LiCl c) H 2 Xe H 2.
At a given pressure, the condensation point for a substance is the same as its. The relationship between pressure change and temperature change during evaporation (in general:. They give the temperature at which the vapor pressure of.
The normal boiling point of a liquid is the temperature at which the vapor pressure is equal to _____. (c)What happens to a gas if you put it under extremely high pressure?. Which has a higher enthalpy of vaporization?.
It's impossible to know without more information. The change of a substance directly from a solid to a gas or vapor is. Is the point below condensing temperature of a substance 10°F- 15°F.
All boiling points below are normal/atmospheric boiling points:. Substance A boils at 109. Which of the following nonpolar substances will have the highest boiling point?.
Pure water boils at a temperature of 212º Fat which of the following standard conditions?. A liquid boils when its _____ equals the external pressure. The vapor pressure at the "normal" boiling point is 1 atmosphere.In everday life a substance will boil when the vapor pressure is the same as the local atmospheric pressure.
It's impossible to know without more information. Evaporation occurs on the surface.Evaporation only occurs when the partial pressure of vapour of a substance is less than the equilibrium vapor pressure.For example, due to constantly decreasing. 1 "When water boils at 212 F boils, it is only absorbing latent heat." true.
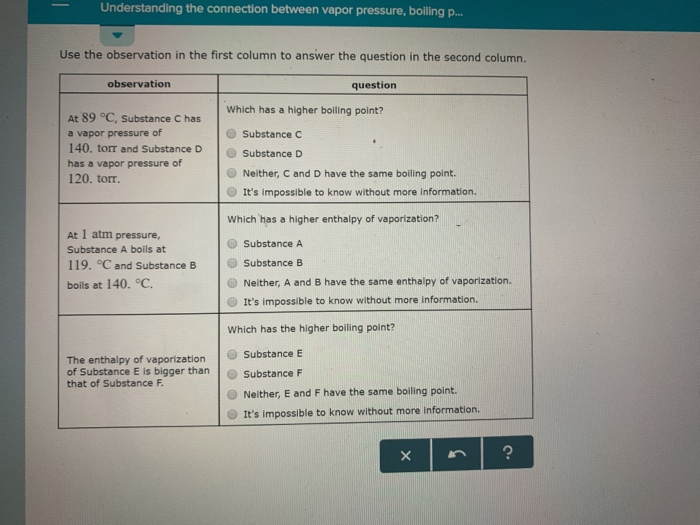
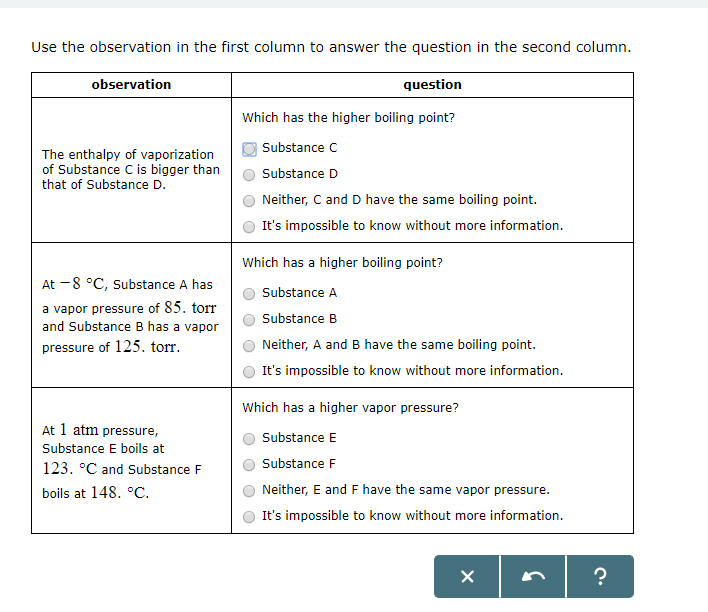
At 5 degree C, Substance A has a vapor pressure of 145, torr and Substance 8 has a vapor pressure of 195 torr. It's impossible to know without more information. 175 CC 17) If this substance was at a pressure of 2.0 atm, at what temperature would 8 18) If this substance was at a pressure of 0.75 atm, at what temperature would it hi6ttQ.
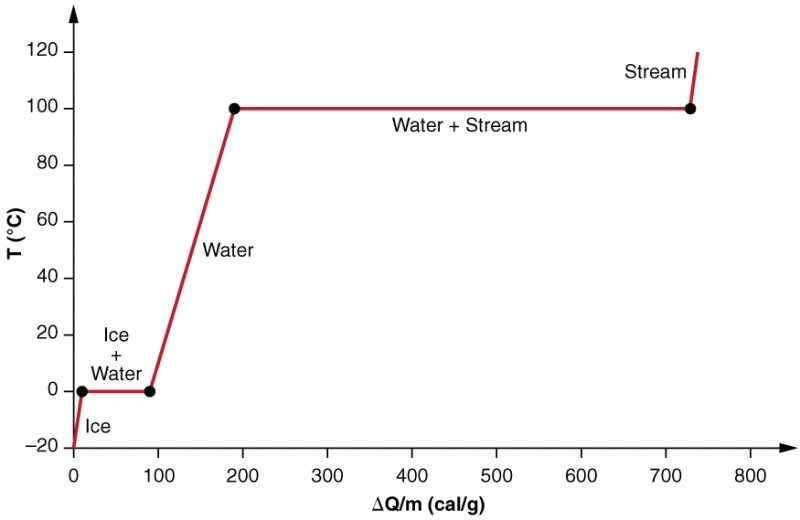
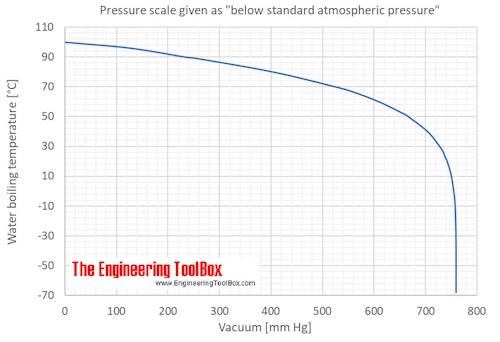
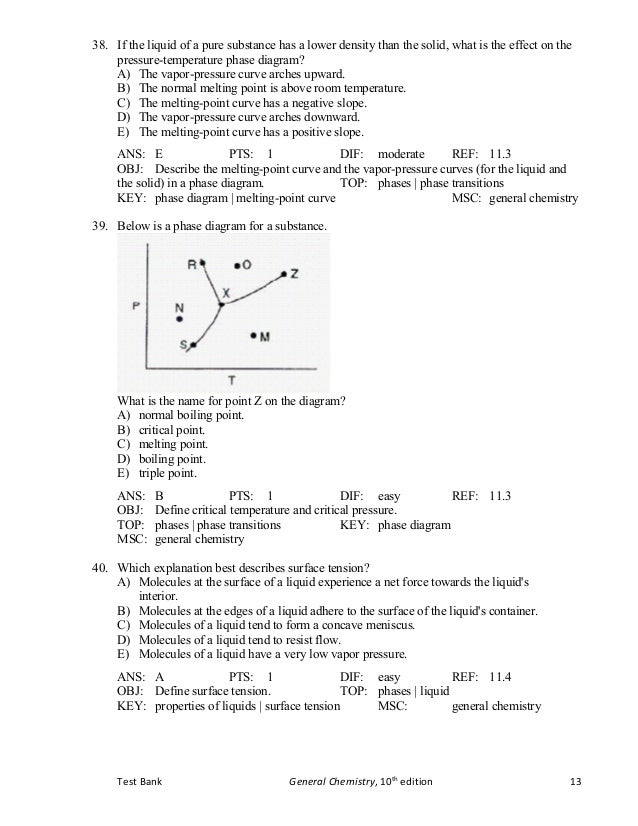
For example, water boils at 100 °C (212 °F) at sea level, but at 93.4 °C (0.1 °F) at 1,905 metres (6,250 ft) altitude. Notice that at stage II and IV, when a substance hits its melting point and boiling point, no change in temperature happens. The temperature will also decrease since the boiling or saturation temperature of a pure substance depends on pressure.
E) Raising the pressure from point E to point C causes the substance to condense. Degree C and Substance F boils at - 87 degree C. I believe the boiling point for brine, or salty water, is 117 degrees Celsius.
The boiling point is the easier concept to think about. For example, water is not readily volatile at room temperature and needs to be heated in order to evaporate. Which has a higher enthalpy of vaporization?.
At 1 atm pressure. Molecules in the liquid escape as a gas at the same rate at which gas molecules stick to the liquid, or form droplets and become part of the liquid phase. Substance C Substance D Neither, C and D have the same enthalpy of vaporization.
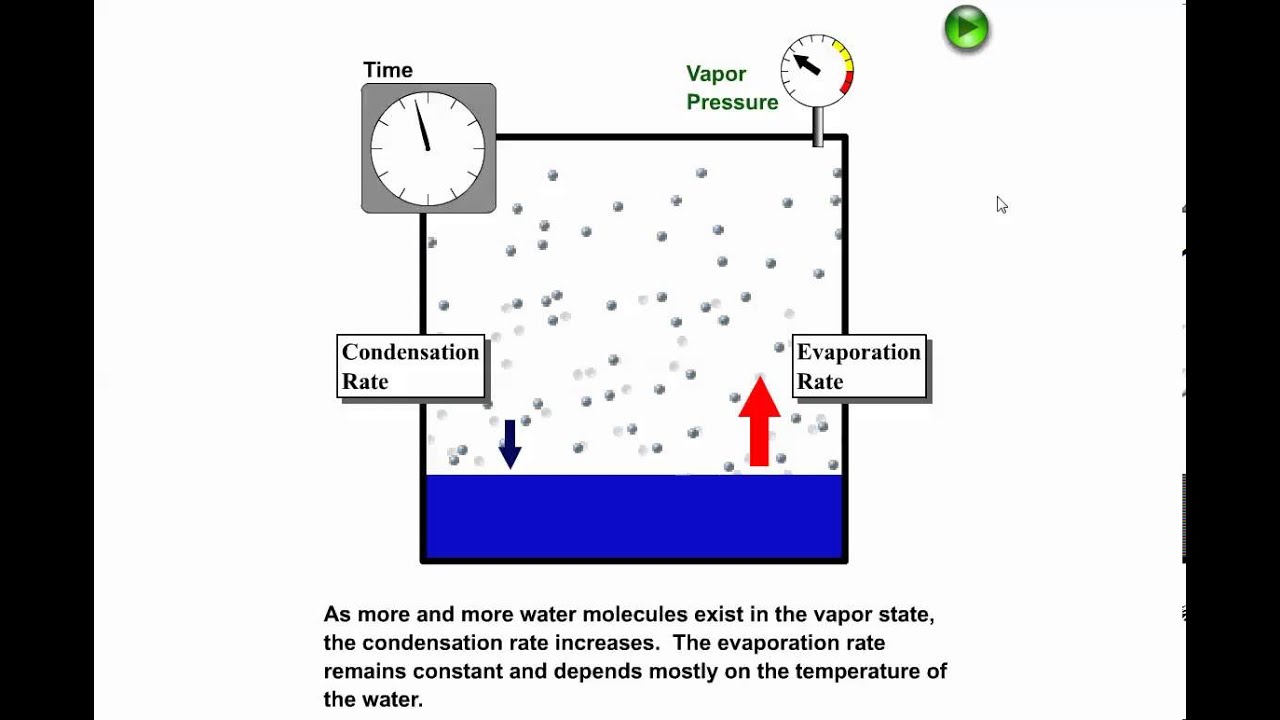
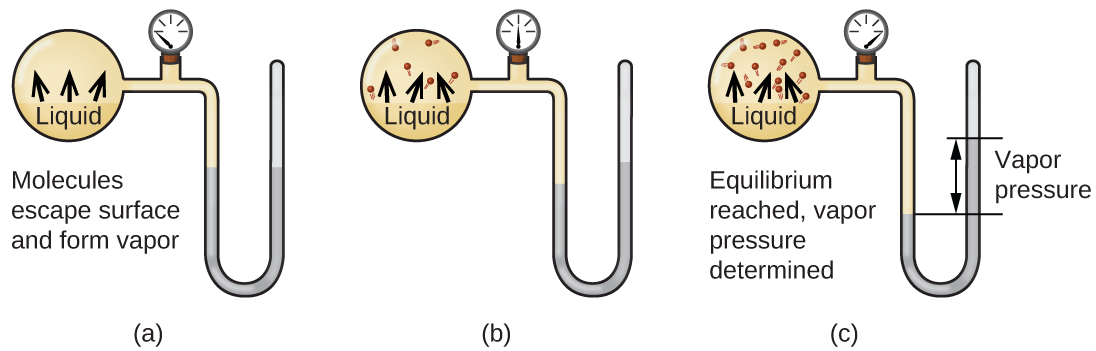
The vapour pressure is the pressure exerted when the molecules leave the surface at the same rate as they return. The boiling point of a substance is the temperature at which the vapor pressure of the liquid is equal to the surrounding atmospheric pressure, thus facilitating transition of the material between gaseous and liquid phases. Evaporation is a phase transition from the liquid phase to vapour (a state of substance below critical temperature) that occurs at temperatures below the boiling temperature at a given pressure.
Increasing pressure usually increases the boiling point of a liquid. If a substance is in a closed container at the boiling point, then the liquid is boiling and the gas is condensing at the same rate without net change in their relative amount. B) the temperature at which the vapor pressure of a substance equals 1 atm.
E) the sum of the enthalpies of vaporization and fusion at 298 K. A boiling liquid expanding vapor explosion (BLEVE, / ˈ b l ɛ v iː / BLEV-ee) is an explosion caused by the rupture of a vessel containing a pressurized liquid that has reached temperatures above its boiling point. Also described was the use of heating and cooling curves to determine a substance’s melting (or freezing) point.
Normally water boils at standard pressure of 29. Vapor pressure is equal to or greater than the external pressure C. > Vapour Pressure Some of the molecules at the surface of a liquid have enough kinetic energy to escape into the atmosphere.
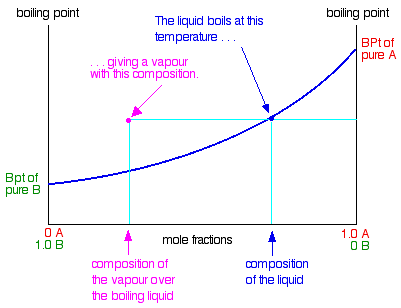
Ton-and Substance B. The Boiling Point is the point at which a substance at liquid state boils. The normal boiling point is a more useful value when comparing different liquids, since boiling is affected by altitude and pressure.
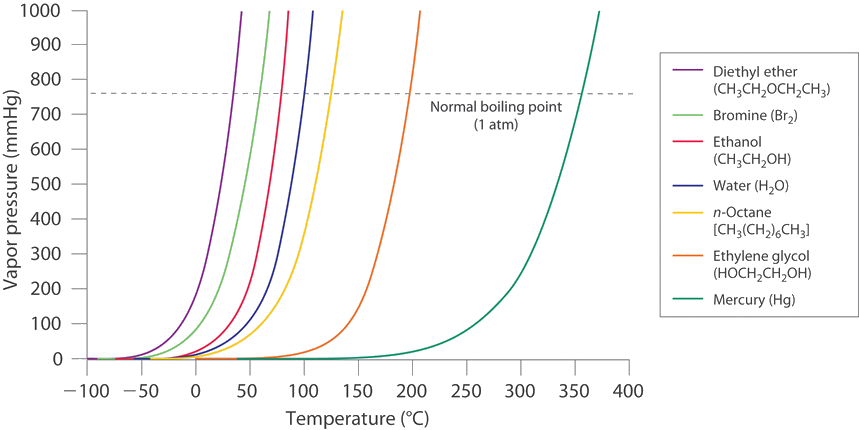
At 1 atm pressure, Substance E boils at - 50. A liquid boils when it's A. The boiling pointof a liquid is the temperature at which its vapor pressure is equal to the pressure of the gas above it.The normal boiling pointof a liquid is the temperature at which its vapor pressure is equal to one atmosphere (760 torr).
At that point, it is possible to change all of the substance to ice, water, or vapor by making arbitrarily small. Which has a higher vapor pressure?. A substance with a lower boiling point has higher volatility and vapour pressure.
For water, it's the range 0-100 °C (32-212 °F) For water, it's the range 0-100 °C (32-212 °F) A = 8., B = 1730.63, C = 233.426 , so the Antoine equation is:. The onset of boiling occurs when the vapour pressure inside the bubble equals the external pressure that acts to collapse it. Substanc E Substance F Neither, E and F have the same enthalpy of vaporization.
A) the pressure of a gas when its temperature reaches 373.15 K. Because the boiling point of a liquid rises with pressure, the contents of the pressurized vessel can remain liquid so long as the vessel is intact. It boils at about 100 degrees celcious ;) lolz The melting point of a solid chemically pure substance is a temperature at which the substance can change from a solid to a liquid phase by absorbing.
C) the temperature at which water boils. The temperature will also increase since the boiling or saturation temperature of a pure substance depends on pressure. 32.0135 °F) and a partial vapor pressure of 611.657 pascals (6. mbar;.
The change of state from a gas to a liquid. The vapor pressure of a liquid can be determined by a device called a _____ manometer. The rate of change of the boiling-point absolute temperature T b of a pure substance with pressure is given by the equation below.
Energy is still being added to the substance, but the temperature doesn. Per 1000 feet increase in elevation. This means that the vapor pressure of water is 1 atm or 760 mmHg at 100 оC.
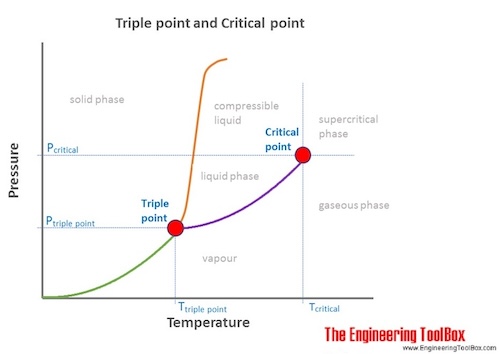
D) At a higher temperature and pressure than point D, the substance exists as a supercritical fluid. Substance A Substance B Neither, A and B have the same vapor pressure. 11.12 Arrange substances Ga, Ne, and Br 2 in order of increasing boiling point.
These molecules exert a pressure on the walls of a closed container. 16) If this substance was at a pressure of 2.0 atm, at what temperature would it melt?. A way to think about it is that the molecules of the liquid need more energy to break into the gas phase when the more molecules are hitting the surface of the liquid with more e.
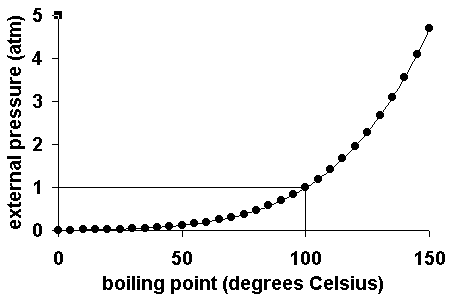
Air pressure and boiling point. Considering the definition of boiling point, plots of vapor pressure versus temperature represent how the boiling point of the liquid varies with pressure. Boiling point of water below sea level.
See spelling differences) or equilibrium vapor pressure is defined as the pressure exerted by a vapor in thermodynamic equilibrium with its condensed phases (solid or liquid) at a given temperature in a closed system.The equilibrium vapor pressure is an indication of a liquid's evaporation rate. H2 CH4 C6H12O6 C3H6. Boiling point only occurs when heat is applied to the liquid substance;.
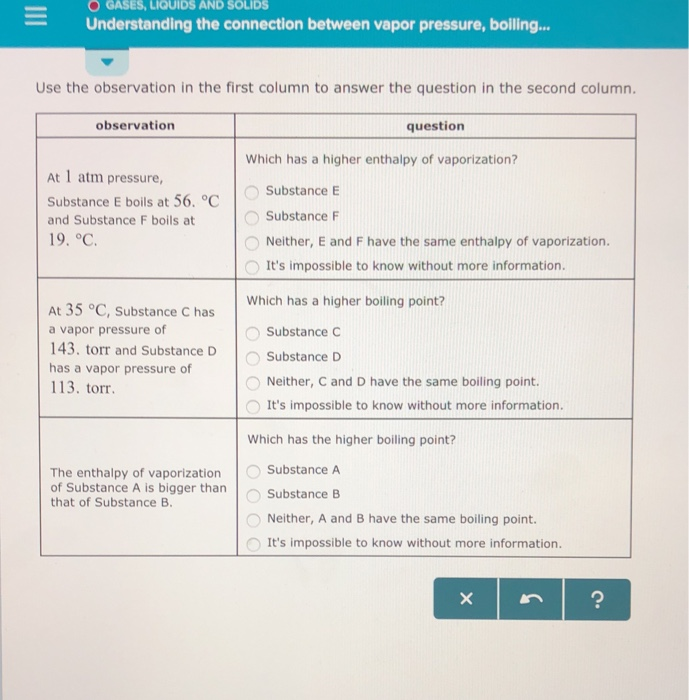
At a constant pressure the volume of gas varies as to the absolute temp and at constant volume the pressure of the gas varies directly with the absolute temp. As you go higher above sea level the _____ decreases and the _____ of a substance gets lower. At 1 atm pressure, Substance C boils at -36 degree C and Substance D boils at -65 degree C Which has a higher enthalpy of vaporization?.
Degree C Which has a higher vapor pressure?. Xe, H 2, H 2 O, LiCl, H 2 S. 1013,25 hPa) and enthalpy of vaporization (molar heat of evaporation), then we can estimate the boiling point under another, selected pressure.;.
When you have a liquid (in 1 atmosphere of air pressure) we define its boiling point when its vapor pressure is equal to atmospheric pressure. The amount of heat needed to change the temperature of a substance will vary with the types of substance. The vapor pressure of a substance is related to temperature, so increasing the temperature increases the vapor pressure till it =1 atmosphere and.
D) the pressure at which a liquid boils at 273.15 K. The normal boiling point is defined as. The boiling point decreases as the vapour pressure increases.
The volatility of a substance is affected by the strength of intermolecular forces. At 1 atm pressure, Substance C boils at 10. Its temperature reaches a point where the liquid’s vapor pressure is the same as the pressure of the surrounding gases.
To be more specific, the boiling point of a substance is the temperature at which both its liquid and vapor or gas states exist in equilibrium. HBr, HCl, HF, HI. Thus any given liquid has an infinite number of boiling points depending upon the pressure applied.
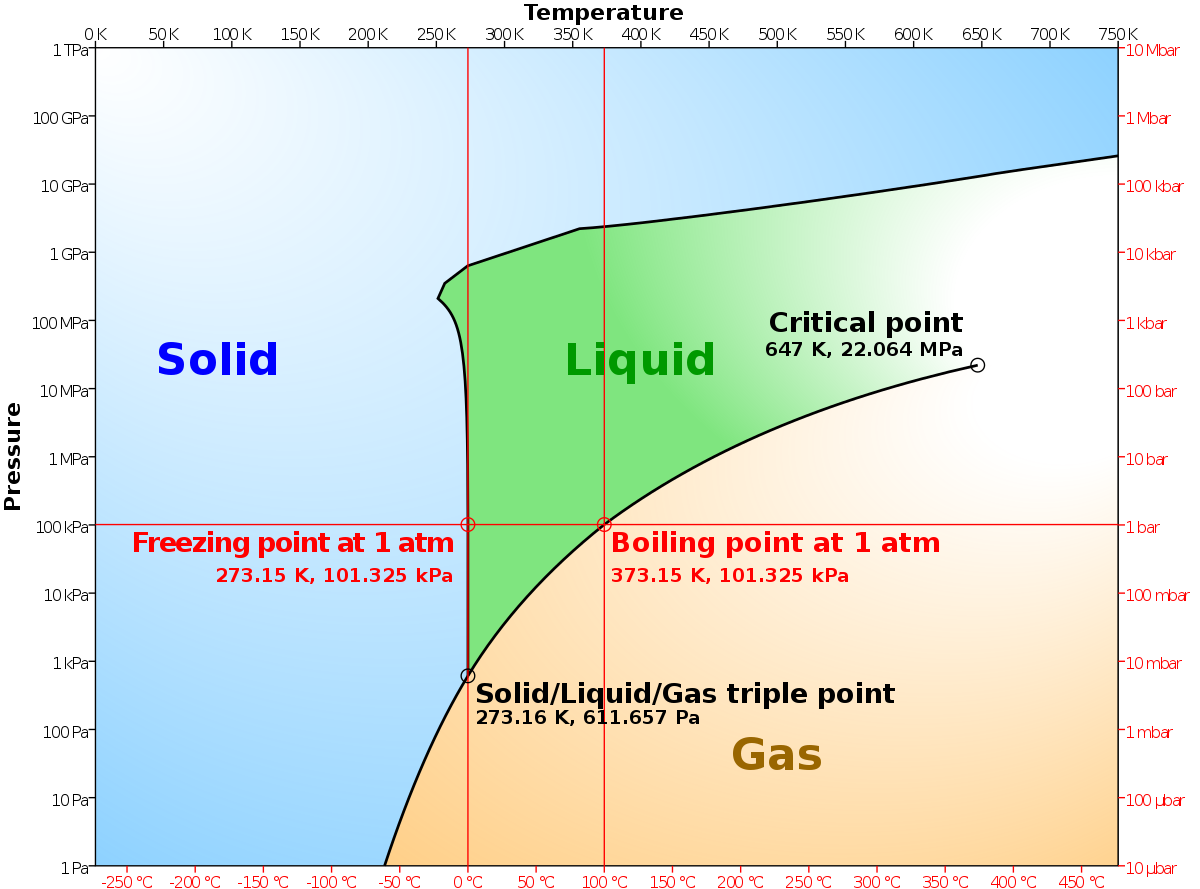
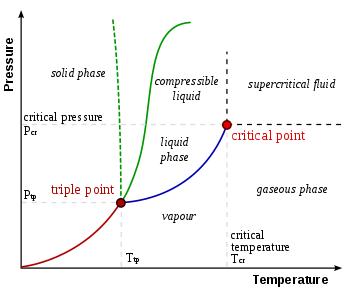
The enthalpy of vaporization of Substance E is smaller than that of Substance F. The single combination of pressure and temperature at which liquid water, solid ice, and water vapor can coexist in a stable equilibrium occurs at approximately 273.1575 K (0.0075 °C;. At 1 atm pressure, Substance E boils at - 50.
It relates to the tendency of particles to. The boiling point of a substance is the temperature at which the liquid phase of the substance boils to becomes a gas (or the gas phase of the substance condenses to become a liquid). Some other normal boiling points are 111.1 K (−162°C) for methane (CH 4), 450°C for triacontane (n-C 30 H 62), 1465°C for sodium chloride (NaCl), and 5555°C for tungsten (W).
One for describing the vapor pressure curve up to the normal boiling point. Degree C and Substance B boils at 125. 11.13 At standard temperature and pressure the molar volume of Cl 2 and NH 3 gases are 22.06 L and 22.40 L.
At 60 degree C, Substance A has a vapor pressure of 129. Atmospheric pressure in inches of mercury (" Hg) decreases by _____ inch(s) per 1000 feet increase in elevation. 11.11 Arrange substances CCl 4, Si, and Ar in order of increasing boiling point.
Degree C and Substance D boils at - 23. Substanc E Substance F Neither, E and F have the same enthalpy of vaporization. The atmospheric pressure at sea level is equal to 101,325 Pa (pascal).
At a pressure greater than 1 atm, water boils at a temperature greater than 100°C because the increased pressure forces vapor molecules above the surface to condense. Although we usually cite the normal boiling point of a liquid, the actual boiling point depends on the pressure. Elevation in boiling point required (ΔT b) =100- 99.
Vapor pressure is exactly 1 atm B. Water boils when the vapor pressure of the water gets to be as big as the pressure of the atmosphere. It's different from the simple definition of boiling point in that the pressure is defined.
Vapor pressure (or vapour pressure in British English;. The temperature that the liquid has to reach to be at Boiling Point (B.P) ranges, it is different for each liquid. To understand it more clearly, recall that the boiling point of water is 100 оC at 1 atm.
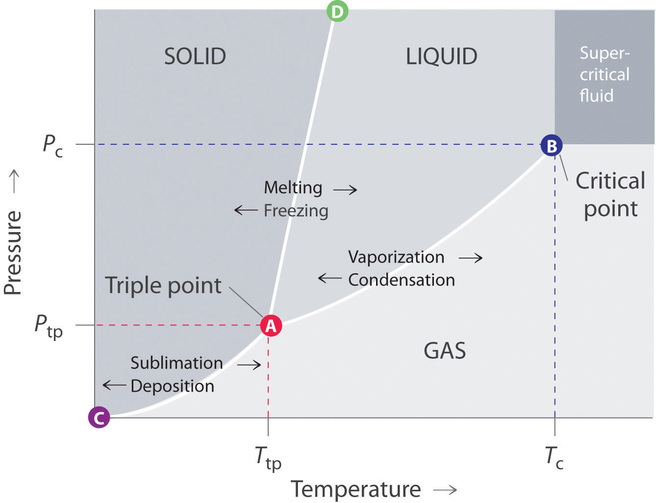
If we know the boiling point of the substance at some specific pressure (tables usually give the value under the so-called normal pressure i.e. Suppose you have a pure substance at three different sets of conditions of temperature and pressure corresponding to 1, 2 and 3 in the next diagram. Temperature is equal to 273 K (standard temperature).
Increasing the external pressure requires a greater matching vapour pressure that is only provided at a higher vapour (and liquid) temperature as the molecules mean speed is increased. For a given pressure, different liquids will boil at different temperatures. Substance E Substance F Neither, C and D have the same boiling point.
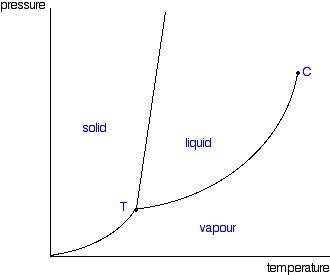
Degree C and Substance F boils at - 87 degree C. Normal boiling point is the temperature at which a liquid boils at 1 atmosphere of pressure. Under the set of conditions at 1 in the diagram, the substance would be a solid because it falls into that area of the phase diagram.
A liquid at high pressure has a higher boiling point than when that liquid is at atmospheric pressure.
Solved Understanding The Connection Between Vapor Pressur Chegg Com

Aleks Understanding The Connection Between Vapor Pressure Boiling Point Etc Youtube
Http Users Wfu Edu Kingag 111 Examkeys 09 Exam3 Pdf
At Pressure Substance E Boils At And Substance F Boils At のギャラリー

Tb Chapter11 bbbbbbbbbbbbbbbbbbbbbbbb
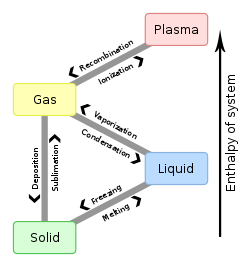
Phase Changes Boundless Chemistry
Phase Diagram Wikipedia

Explain The Following The Temperature Remains Constant During Boiling Of A Liquid

What Happens To A Boiling Temperature As Pressure Decreases
Www Bscsd Org Site Handlers Filedownload Ashx Moduleinstanceid 374 Dataid 1504 Filename Apchemistrycompletedhomeworkliquidssolids 21 Pdf

Does Salt Make Water Boil Faster Live Science

Solved Which Has A Higher Enthalpy Of Vaporization At 1 Chegg Com

Phase Change And Latent Heat Physics

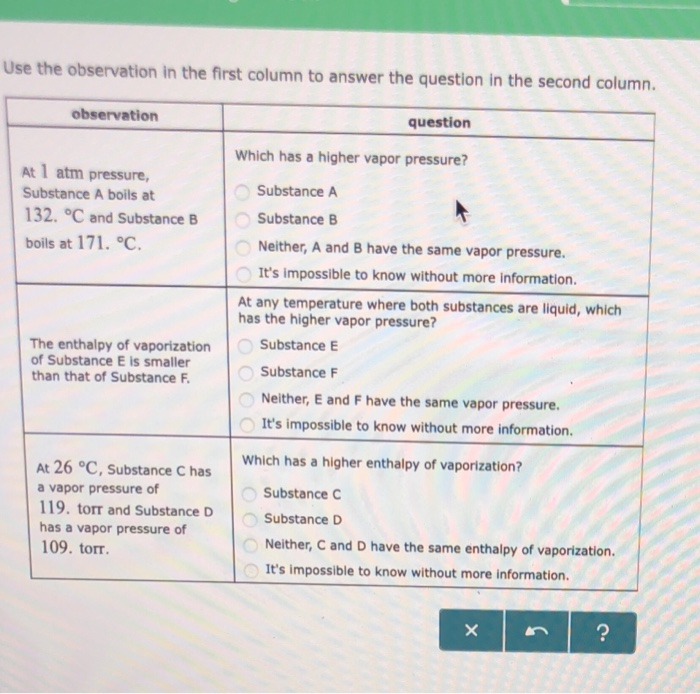
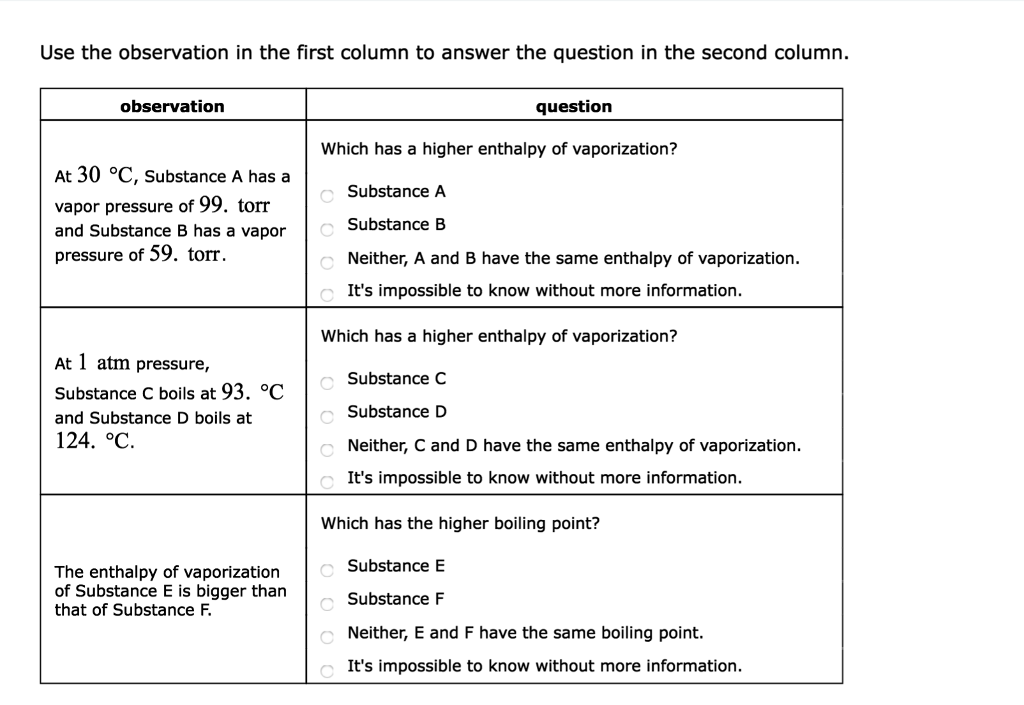
Solved Use The Observation In The First Column To Answer Chegg Com
Solved Use The Observation In The First Column To Answer Chegg Com

Water Students Britannica Kids Homework Help
Solved The Enthalpy Of Vaporization Of Substance E Is Sma Chegg Com

Attractions And Boiling
Http Www Srvhs Org Staff Teachers Jleach Ch 10 review phase change answers0001 Pdf
2

What Are The Freezing Melting And Boiling Points Of Solids Liquids And Gases Owlcation Education
Phase Change And Latent Heat Physics

Boiling Point Accessscience From Mcgraw Hill Education

Melting Point Wikipedia

Specific Heat Heat Of Fusion And Vaporization Example Video Khan Academy

Boiling Chemistry Libretexts
Www Studocu Com En Us Document Mississippi College General Physics Tutorial Work Chapter 11 Answers 19 05 15 22 08 47 Utc View

Lng What Is Boil Off Gas And What Does It Do Fluenta
Characteristics Of The Solid Liquid And Gaseous States
Http Users Wfu Edu Kingag 111 Examkeys 09 Exam3 Pdf
Boiling Point Elevation
Boiling
Water Boiling Points At Vacuum Pressure
Characteristics Of The Solid Liquid And Gaseous States

Boiling Chemistry Libretexts
Solved Use The Observation In The First Column To Answer The Question In The Second Column Which Has A Higher Vapor Pressure At 1 Atm Pressure S Course Hero

Heating Curve For Water Introduction To Chemistry
Solved Use The Observation In The First Column To Answer Chegg Com
Solved Gases Liquids And Solids Understanding The Connec Chegg Com
Tb Chapter11 bbbbbbbbbbbbbbbbbbbbbbbb
7 2 Vapor Pressure Chemistry Libretexts

Phase Changes Boundless Chemistry
11 6 Properties Of Liquids Chemistry Libretexts

Solved Use The Observation In The First Column To Answer Chegg Com
Unit Operations In Food Processing R L Earle
Q Tbn And9gcslxxohf6s Byidgpakdcgmarcsqcauhrjvta Usqp Cau
Solved Use The Observation In The First Column To Answer Chegg Com
Phase Diagrams Of Pure Substances

Melting Point Freezing Point Boiling Point
2

Tb Chapter11 bbbbbbbbbbbbbbbbbbbbbbbb
2
Http Www2 Chem Uic Edu Tak Chem Solutions set 10 Pdf

Boiling Point Wikipedia

You May Write On This Test But Only The Scantron Form Will Be Scored
/BoilingWater-58dd1c2a5f9b5846837d2a23.jpg)
What Is The Boiling Point Of Water

15 2d Understanding The Connection Between Vapor Pressure Boiling Point And Enthalpy Of Vaporizati Youtube
Http Cdochemistrychristman Pbworks Com W File Fetch Ap chemistry unit 7 part 1 intermolecular forces
Critical Temperatures And Pressures For Some Common Substances

Vapor Pressure Video States Of Matter Khan Academy

Solved Use The Observation In The First Column To Answer Chegg Com
Triple Point Wikipedia
Chemfall09 Pbworks Com F Problem Set 4 Solutions Pdf

Heat Of Vaporization Of Water And Ethanol Video Khan Academy

Enthalpy Of Vaporization Wikipedia

Boiling Melting Points And Intermolecular Forces Youtube

Gases Liquids And Solids Understanding The Connection Between Use The Observation In The First Column Homeworklib
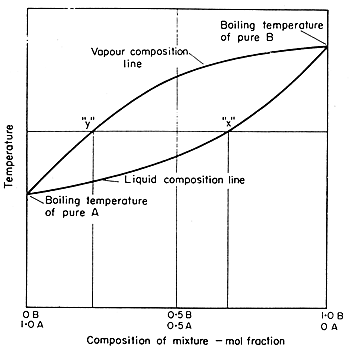
Raoult S Law And Ideal Mixtures Of Liquids
11 5 Vapor Pressure Chemistry Libretexts

Unit 2 Flashcards Quizlet
Http Www2 Chem Uic Edu Tak Chem Solutions set 10 Pdf
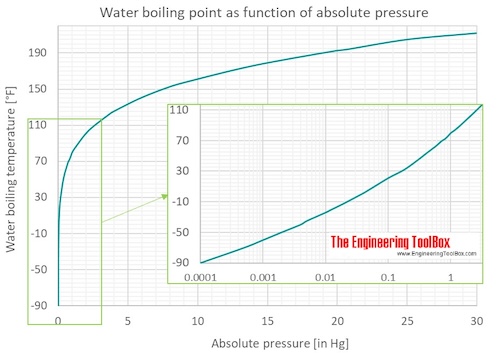
Water Boiling Points At Vacuum Pressure
Define Melting Point And Boiling Point What Is The Difference Quora
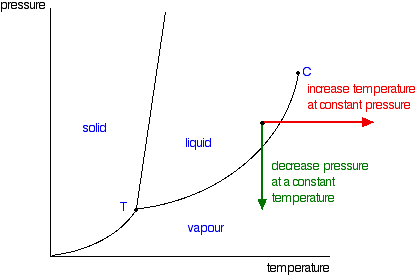
Phase Diagrams Of Pure Substances

Gases Liquids And Solids Understanding The Connection Between Use The Observation In The First Column Homeworklib
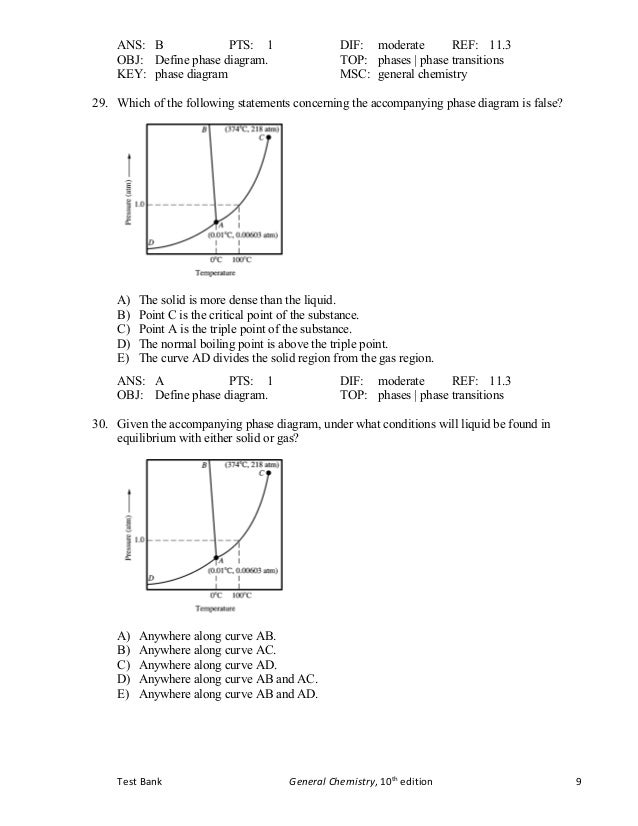
Tb Chapter11 bbbbbbbbbbbbbbbbbbbbbbbb
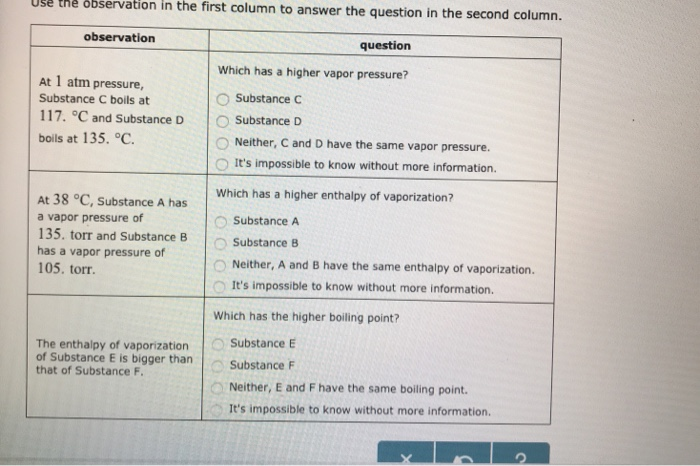
Solved Use The Observation In The First Column To Answer Chegg Com

Chapter 2a Pure Substances Phase Change Properties Updated 9 09

How Do I Rank The Following Compounds From Lowest To Highest Boiling Point Calcium Carbonate Methane Methanol Ch O Dimethyl Ether Ch Och Socratic

Boiling Chemistry Libretexts
Www Ranchorams Org Ourpages Auto 13 12 17 Imfbondingfrmc key Pdf
Www Unf Edu Michael Lufaso Chem46h 46chapter11 Pdf
Solved At 1 Atm Pressure Substance E Boils At 50 Degr Chegg Com

Boiling Point Wikipedia

Phase Diagrams

Boiling Point Definition Examples Temperature Facts Britannica
12 4 Phase Diagrams Chemistry Libretexts

Heat Of Vaporization Chemistry Britannica

Use The Observation In The First Column To Answer The Question In The Second Column Observation Homeworklib
Static1 Buchi Com Sites Default Files Melting And Boiling Point Laboratory Guide From Buchi Pdf 0d24e3a51fedd51c2bbf0e293dc41d211e
Http Www2 Chem Uic Edu Tak Chem Solutions set 10 Pdf
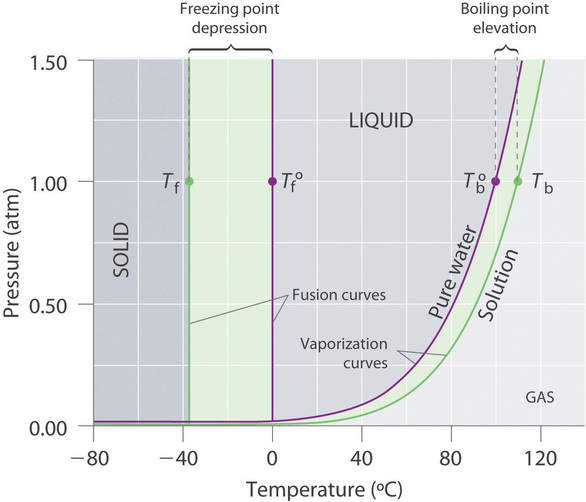
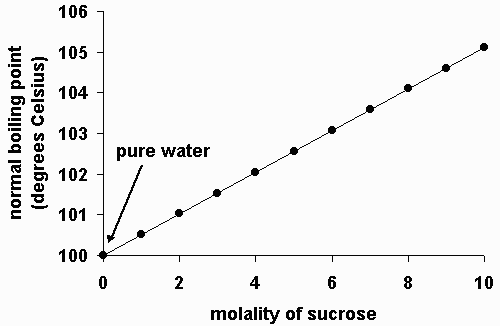
13 8 Freezing Point Depression And Boiling Point Elevation Of Nonelectrolyte Solutions Chemistry Libretexts

Tb Chapter11 bbbbbbbbbbbbbbbbbbbbbbbb

Triple Point Wikipedia

Vapor Pressure Wikipedia
Www Plps K12 Org Site Handlers Filedownload Ashx Moduleinstanceid 24 Dataid 3863 Filename Practice test chapter 10 key Pdf
Www Plps K12 Org Site Handlers Filedownload Ashx Moduleinstanceid 24 Dataid 3850 Filename Imfa practice ws 1 key Pdf

Chapter 2a Pure Substances Phase Change Properties Updated 9 09
Boiling Point Wikipedia
Solved Use The Observation In The First Column To Answer Chegg Com

Equilibrium Vapor Pressure An Overview Sciencedirect Topics




